Titanium
Titanium is a strong metal that exhibits good resistance to atmospheric corrosion. It is an element in period 4 and group 4 of the periodic table, with an atomic number of 22. Titanium alloy is an alloy based on titanium metal and formed by adding other elements (such as aluminum, vanadium, molybdenum, zirconium, etc.). Titanium alloys are known for their unique combination of properties, including high strength, low density, good corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, making them an ideal material choice in many fields.
 #Application areas
*Aerospace: Titanium is widely used in aircraft, missile and rocket manufacturing due to its light weight, high strength and heat resistance.
#Application areas
*Aerospace: Titanium is widely used in aircraft, missile and rocket manufacturing due to its light weight, high strength and heat resistance.
- Marine and industrial: Titanium can withstand corrosion from marine environments and industrial sulfur compounds, making it suitable for use on ships, offshore platforms and industrial equipment.
- Medical field: Titanium’s biocompatibility makes it an ideal material for artificial joints, bone nails and other medical implants.
- Automotive industry: Titanium is used to make engine components such as connecting rods, valves, etc. because of its durability, lightweight, high strength and resistance to hot corrosion.
- Construction Industry: Titanium alloys are increasingly popular in building structures, infrastructure and special applications due to their beauty, durability and corrosion resistance.
- Consumer products: Titanium is also found in a variety of consumer products such as jewelry, watches, eyewear, bicycles, and clocks.



Processing method
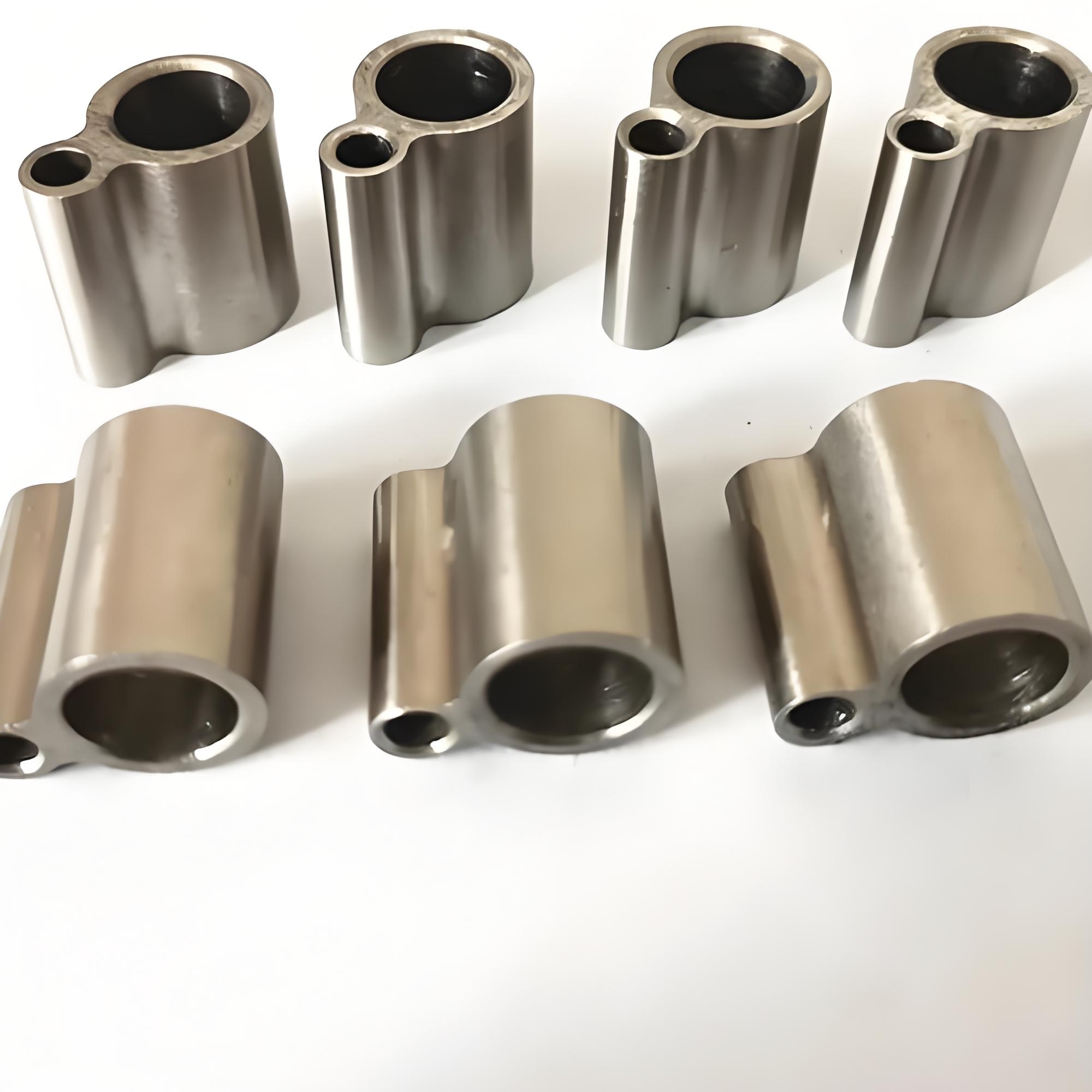
CNC
For titanium alloys, CNC machining is a common manufacturing method because the high strength and corrosion resistance of titanium alloys make them very popular in many industrial applications. CNC machine tools can process titanium alloys accurately according to design drawings, achieving extremely high precision requirements. CNC machined titanium alloy parts usually have a better surface finish.

3D printing
Titanium 3D printing, also known as titanium additive manufacturing, is a technology that builds three-dimensional objects layer by layer. This technology is particularly useful for designs that are complex or difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. The cost of titanium alloy powder and 3D printing equipment is higher. Printed titanium parts may require heat treatment and surface treatments to improve performance. Compared to some plastic materials, titanium alloys may be slower to 3D print. Common titanium alloy 3D printing technologies include electron beam melting (EBM), selective laser melting (SLM), and direct energy deposition (DED).

Post-processing
- Deburring: Use hand tools, mechanical or chemical methods to remove sharp edges and burrs generated after processing.
 *Sandblasting: Improves surface finish and removes minor machining marks.
*Sandblasting: Improves surface finish and removes minor machining marks.

- Anodizing: Improves the corrosion resistance and wear resistance of titanium alloy, and can also be used to increase surface color.