Aluminum
AL, or aluminum alloy, is an alloy material based on aluminum and made by adding a certain amount of other elements (such as copper, magnesium, manganese, silicon, etc.). The grades of aluminum alloys are represented by the 2XXX~8XXX series, where the second letter of the grade indicates the modification of the original alloy.
| Serial number | Main alloying elements | Features | Typical applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1xxx | xx% high purity aluminum | High electrical and thermal conductivity, excellent corrosion resistance | Wire conductors and chemical processing equipment |
| 2xxx | Copper | High strength-to-weight ratio, low corrosion resistance | Truck wheels and suspension systems, aircraft fuselages and wings |
| 3xxx | Manganese | Moderate strength and good machinability. | General sheet work, recreational vehicles, electronic products. |
| 4xxx | Silicon | Low melting point and thermal expansion, high wear resistance. | Welding wire and brazing alloys, construction applications, forged engine pistons. |
| 5xxx | Magnesium | Moderate to high strength, good weldability, good corrosion resistance. | Household appliances, automotive parts, marine components. |
| 6xxx | Silicon and magnesium | Moderate strength with good formability, weldability, machinability and corrosion resistance. | Structural applications, building profiles, leisure equipment. |
| 7xxx | Zinc | Moderate to very high strength. | Airframe structures, mobile equipment, high stress components. |
| 8xx.x | Tin | Low friction. | Bearing and bushing applications. |
Material properties
- Lightweight and high strength: Aluminum alloys have a low density of about 2.7 g/dm³, which is 1/3 of copper or iron, and have high specific strength.
- Good electrical and thermal conductivity: The thermal and electrical conductivity of aluminum are second only to copper, about 3 to 4 times that of steel.
- Easy to recycle: Aluminum is not easy to deteriorate after long-term use, has a low melting point, and can be recycled.
- Non-magnetic: Aluminum is a non-magnetic body and will not be affected by the surrounding magnetic field.
- Low temperature resistance: Aluminum increases its strength at low temperatures without brittleness, making it an ideal material for low-temperature devices.
- Good reflectivity: Aluminum has good reflective properties for light, heat, and radio waves.
Processing characteristics
- Good ductility: Suitable for plastic processing, it can be processed into various shapes, from thin sheets to complex shapes.
- Suitable for casting processing: Due to its low melting point and good fluidity, it is suitable for casting processing.
- Easy to cut and weld: Aluminum can be easily cut and welded.
Application areas
- Aerospace: Used to manufacture aircraft fuselages, engine parts, satellites, etc.
- Automobile manufacturing: Used for automobile bodies, engine parts, suspension systems, etc. to reduce the weight of the car and improve fuel efficiency.
- Construction engineering: Used for bridges, high-rise buildings, heavy machinery parts, etc.
- Electronic equipment: Used for wires, busbar connectors, electronic components, etc.
- Marine engineering: Due to its corrosion resistance, it is used in marine engineering, chemical equipment and other fields.
- Low temperature equipment: used in cold storage, freezer, LNG storage tank, etc.

Processing method
- Stamping: A workpiece forming processing method that applies external force to plates, strips, pipes and profiles through presses and molds to cause plastic deformation or separation.
- Machining: Mainly uses general machine tools such as lathes, milling, planing, drilling, and grinding to process mold parts. It can also be called CNC precision machining or automatic lathe machining, CNC lathe machining, etc.
- Precision casting: Parts obtained by this method generally do not need to be machined again, such as investment casting, pressure casting, etc. Powder metallurgy: solid powder is mixed with organic binder evenly, and after granulation, it is injected into the mold cavity by injection molding machine under heating and plasticization state for curing and forming, and then the binder in the formed blank is removed by chemical or thermal decomposition method, and finally the final product is obtained by sintering and densification.
Post-processing method
-
Anodizing: The purpose of aluminum surface treatment oxidation is divided into two aspects, enhancing physical properties and achieving coloring purpose. Detailed explanation of the sealing process of new aluminum and aluminum alloy after anodizing treatment. Regardless of whether the film after anodizing is colored or not, the aluminum alloy sealing treatment process must be carried out.

-
Sandblasting: used to overcome and cover up some defects of aluminum alloy produced during mechanical processing, and to meet some special requirements of customers for product appearance.

-
Electroplating: more common, there is also a process of electroplating after grinding.

-
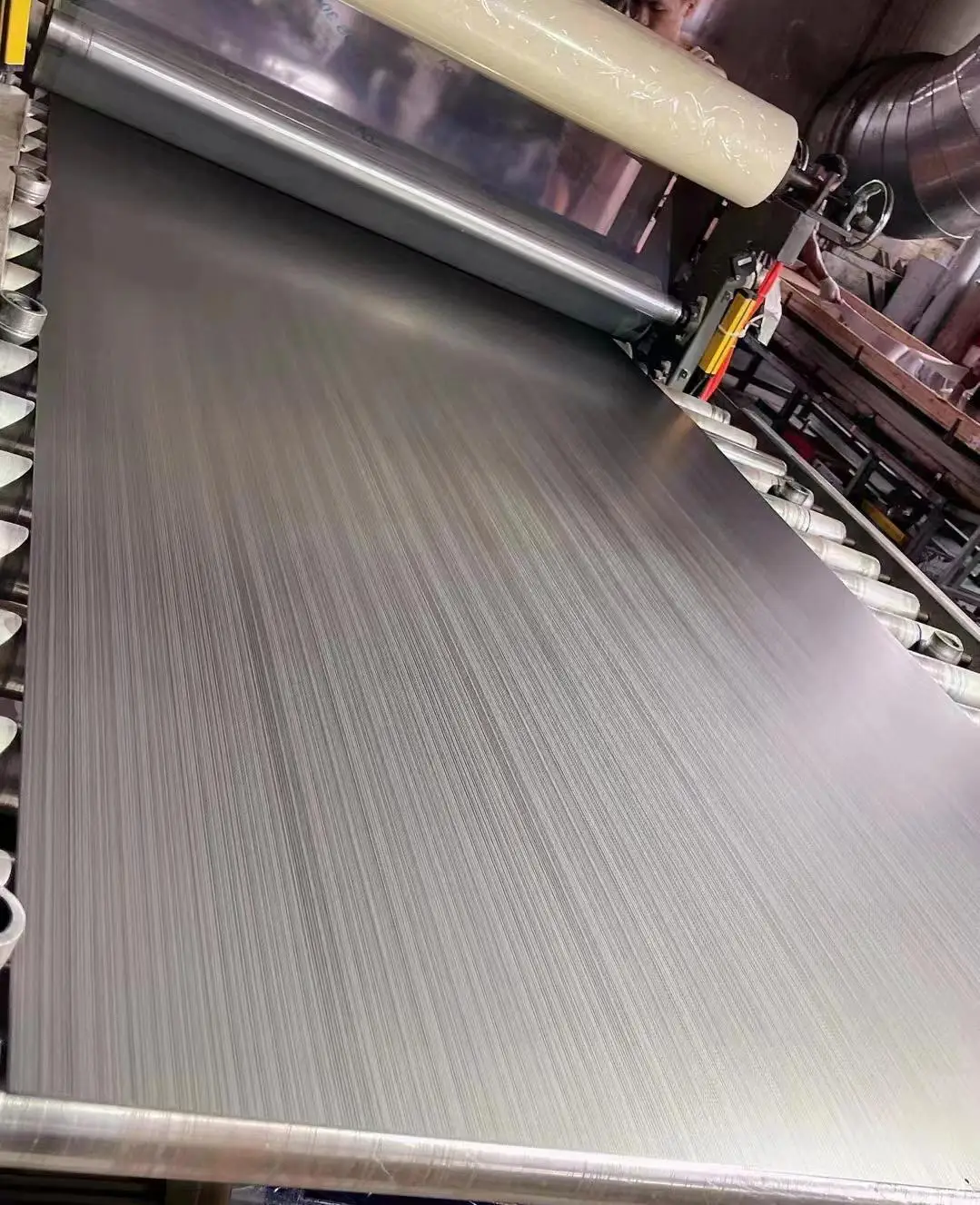
Brushing: similar to car grain, both form smooth continuous lines on the surface, the difference is that car grain is processed by lathe, while rubbing grain is polished with sandpaper.

-
Polishing: Polish the surface of aluminum alloy products by mechanical, chemical or electrochemical methods to reduce the surface roughness of aluminum alloy products and make the surface of aluminum alloy products smoother and brighter.